In the world of pharmacy, compounding medications play a crucial role in meeting the unique needs of patients. Compounding refers to the process of customising medications by combining different ingredients in specific dosages and forms. This specialised practice allows pharmacists to create personalised medications that are not commercially available or tailor existing medications to suit individual requirements. Understanding the process of compounding medications is essential for both healthcare professionals and patients alike, as it provides insights into the benefits, considerations, and safety measures associated with this practice.
The Role of Compounding Medications in Patient Care
Compounding medications have a long history dating back to the origins of pharmacy itself. In earlier times, pharmacists used to create medications from scratch by combining raw ingredients. With the evolution of the pharmaceutical industry, commercial manufacturing became dominant, leading to a decline in compounding practices. However, the need for customised medications persisted, prompting a resurgence of interest in compounding in recent years.
One of the primary reasons for compounding medications is to meet the unique needs of patients who may require medication in a different strength, dosage form, or combination. For example, a patient with difficulty swallowing pills may benefit from a compounded medication in a liquid form. Likewise, children or elderly patients may require lower doses of certain medications, which can be achieved through compounding. Compounding can also be used to remove allergenic substances, such as dyes or preservatives, from commercially available medications, making them suitable for patients with specific sensitivities.
The Process of Compounding Medications
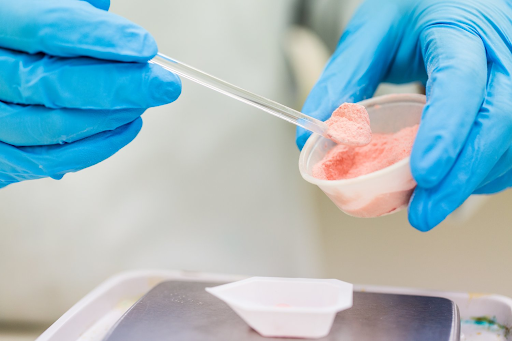
The process of compounding medications involves several key steps. It begins with a prescription from a healthcare professional that specifies the desired medication and any specific requirements. The pharmacist then reviews the prescription and evaluates the patient’s needs to determine the most appropriate compounding method. The pharmacist selects the necessary active pharmaceutical ingredients, excipients, and equipment required for compounding.
Accurate measuring and weighing of the ingredients are essential to ensure the final product’s safety and effectiveness. Pharmacists must follow precise calculations and employ specialised equipment to achieve the desired dosage and consistency. Depending on the required dosage form, compounding can involve various techniques, including mixing powders, dissolving substances, or preparing suspensions, creams, ointments, gels, capsules, or suppositories.
Quality Control in Compounding Medications
Quality control is a critical aspect of compounding medications. Pharmacists must adhere to strict standards to ensure the integrity, potency, stability, and sterility of the compounded products. This involves using high-quality ingredients from reliable sources, following standardised compounding procedures, and regularly testing the final product for quality assurance.
Compounded medications offer several advantages over commercially available products. The customization of medications allows for individualised treatment, catering to patients with specific needs. Compounding can provide alternative dosage forms, making medication administration easier for patients who struggle with traditional formulations. For instance, paediatric patients may find it easier to take medications in the form of flavoured suspensions. Furthermore, compounding medications can address medication shortages, ensuring patients have access to necessary treatments when commercial products are unavailable.
Considerations and Potential Risks in Compounding Medications
However, compounding medications also present certain considerations and potential risks. The customization process introduces an additional level of complexity, requiring expertise and precision from pharmacists. It is crucial to work with qualified compounding pharmacists who possess the necessary knowledge, skills, and experience in this specialised field. Additionally, there may be limitations to what can be compounded, as not all medications or combinations are suitable for compounding. It is important for pharmacists to consider factors such as stability, compatibility, and safety when compounding medications.
Patient safety is of utmost importance in compounding. Compounded medications should be prepared in compliance with applicable regulations and guidelines. Pharmacists should follow good compounding practices and maintain a clean and sterile environment to minimise the risk of contamination. Additionally, proper labelling and clear instructions for use must be provided to ensure patients understand how to take their compounded medications correctly.
Collaboration and Communication in Compounding Medications
Collaboration between healthcare professionals, including physicians, pharmacists, and patients, is crucial to the success of compounding medications. Communication and coordination are essential to ensure that patients’ needs are met, appropriate medications are prescribed, and any potential risks or interactions are identified and addressed. Patients should actively engage with their healthcare providers, providing complete information about their medical history, allergies, and any other relevant factors that may impact the compounding process.
Conclusion
Compound medication pharmacy is a specialised practice that allows pharmacists to customise medications to meet the unique needs of patients. By combining different ingredients, dosages, and forms, compounding enables personalised treatment options that are not commercially available. While compounding offers numerous benefits, it also requires expertise, precision, and adherence to strict quality control measures. Patient safety is paramount, and collaboration among healthcare professionals is essential to ensure the appropriate and safe use of compounded medications. Understanding the process of compounding medications provides valuable insights into this important aspect of pharmacy practice, fostering improved patient care and treatment outcomes.